
This strategy can help you to increase your average order value (AOV) by cross-selling and upselling complementary products. A classic bundle pricing strategy example is when fast-food chains like McDonald's offer meal deals. Whenever you offer two or more products for a single price, you’re using a bundle pricing model. Most brands using this pricing strategy will set a price that’s far higher than the COGS. For example, the watch brand Rolex uses a premium pricing model. Unsurprisingly, premium pricing is most often used by luxury brands in the fashion and hospitality industries. It’s also known as prestige or luxury pricing. The idea is to set a high price to increase the perceived value of a product or service. Premium Pricing StrategyĪ premium pricing strategy is exactly what it sounds like. However, tactics like these don’t work well when your target market is primarily concerned with quality and/or prestige. If people in your target market are attracted to sales and discounts, this pricing strategy may be a good bet. It works by anchoring the price high and then offering a lower price to make the price seem like a good deal. This works because when people read from left to right, the number appears smaller.Īnother psychological pricing tactic is called price anchoring. A common tactic is ‘charm pricing’ - when a price ends in 9, 99, or 95 to make it feel cheaper than it is. This pricing strategy is all about using human psychology principles to increase sales. If you’ve ever walked into a discount store, you’ve experienced psychological pricing firsthand. This pricing strategy also works well when you’re able to price your product or service similar to competitors, in addition to offering extra features, perks, or benefits that your competitors don’t offer.įor example, Shopify’s pricing is very similar to its competitors’ pricing, but the platform provides many more features for the same price. Just be careful not to join a ‘race to the bottom’ - this is when businesses keep undercutting each other in an attempt to win more business but inadvertently drive down profits for everyone. This pricing model works best in a saturated niche where consumers may choose one similar offer over another because of a slightly lower price. You could price your products the same, or slightly higher or lower than your competitors.

When using this pricing strategy, you would research the prices offered by your closest competitors and price your offers similarly. Competitive Pricing StrategyĬompetitive pricing - also known as competition-based pricing - follows the going market rate for a product or service.
Pricing strategy for products software#
It usually doesn’t work very well for more complex products or services, such as software or consulting services. The cost-plus pricing strategy is mostly used by retailers selling many physical products.
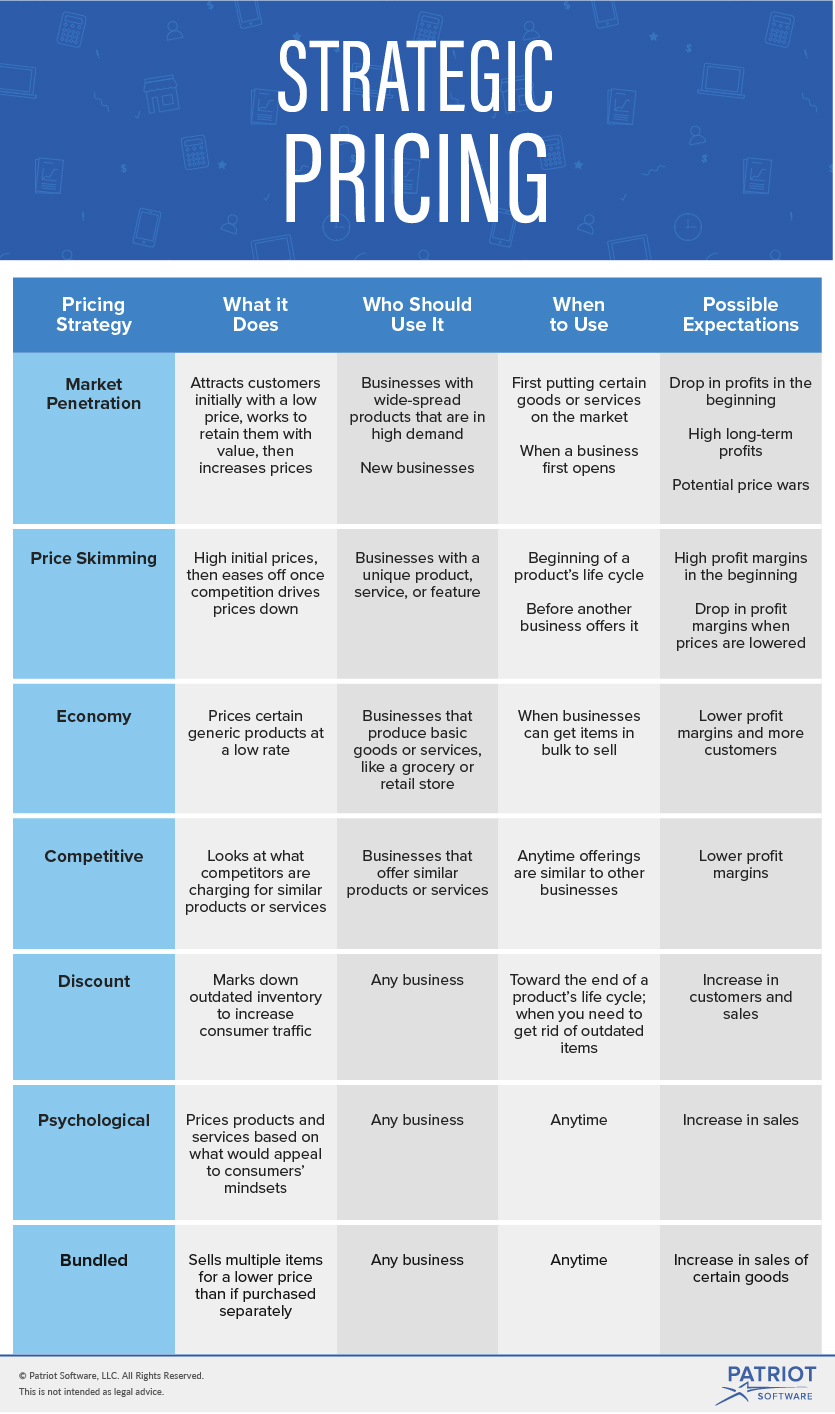
This is why the cost-plus pricing model is often referred to as ‘markup pricing.’ Once you’ve determined the COGS, you would apply a fixed percentage to make a profit.

This includes product sourcing, packaging, shipping, storage, marketing, overheads, and any other cost required to produce and sell the product or service. Here’s how it works: First, you would determine the total cost of producing and selling your product or service - also known as the cost of goods sold (COGS). Cost-Plus Pricing StrategyĪ cost-plus pricing strategy is one of the most straightforward ways to price your offers. Let’s take a closer look at each one so you can understand the differences. The type of pricing strategy that you use will depend on a few factors. Here are 15 types of pricing strategies that we’re going to explore in this article: There are many different types of pricing strategies - each with its advantages and disadvantages. Pricing strategies are designed to maximize both sales and profits. A pricing strategy is a method used to identify the optimum price for a product or service.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
